Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
In today’s fast-paced communication landscape, signal quality is paramount. This is where Dielectric Filters come into play. These devices are designed to enhance the transmission of signals while minimizing interference. By selectively allowing certain frequencies to pass through, they ensure clearer communications.
Dielectric Filters operate on dielectric materials that are both lightweight and efficient. They achieve remarkable performance by reducing signal loss. This makes them crucial for various applications. However, the implementation of these filters is not without its challenges. Selecting the right type, for example, can be complex. Different environments may affect their performance, requiring careful installation and adjustment.
Users often overlook the importance of regular maintenance for Dielectric Filters. Without it, performance may degrade over time. Therefore, understanding the nuances of these filters is vital for maximizing their benefits. Enhanced signal quality not only leads to better communication but also improves overall system efficiency. The knowledge of how to utilize Dielectric Filters effectively opens doors to an improved audio and visual experience.
Dielectric filters are essential components in signal processing. They manage frequency interference. By selectively allowing certain frequencies to pass, they enhance overall signal clarity. This feature is crucial in communication systems like radio or television.
Understanding how dielectric filters work is vital. They rely on the properties of materials that possess high resistance to electric current. This design allows the filters to block unwanted signals. For instance, a well-tuned dielectric filter can eliminate noise effectively, improving transmission quality. However, achieving this requires careful calibration. Small adjustments can lead to significant changes in performance.
It's important to reflect on some challenges. Not all environments suit dielectric filters perfectly. Reflective surfaces can distort signals. Additionally, improper installation can lead to signal degradation. Users must be diligent and attentive to their setup. Every tiny detail matters in achieving optimal performance.
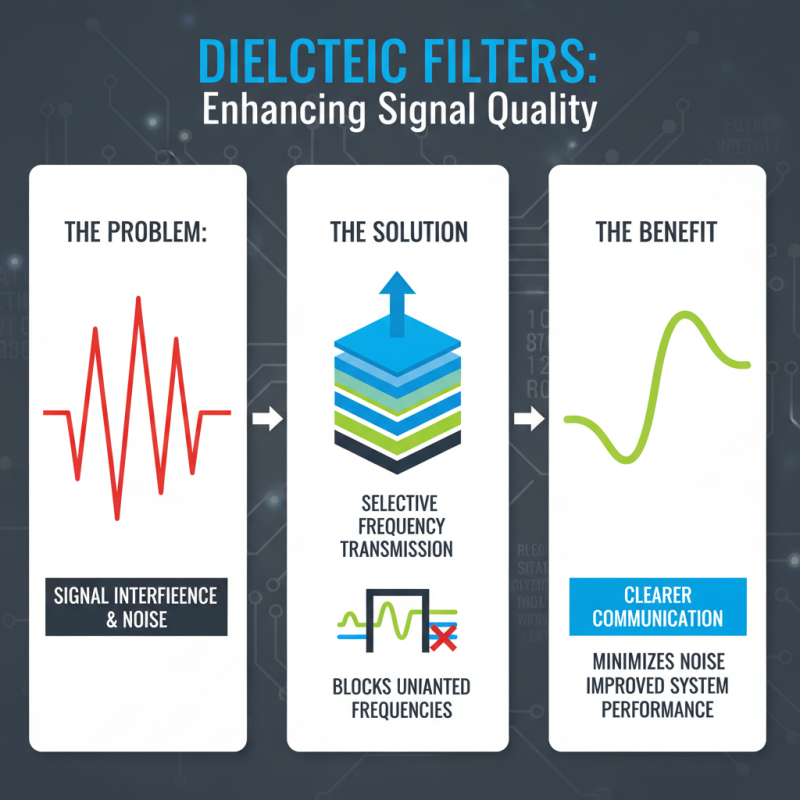
Dielectric filters play a crucial role in improving signal quality. They are designed to selectively transmit certain frequencies while blocking others. This selectivity helps minimize noise in communication systems. Many systems struggle with interference, making dielectric filters an essential component.
The effectiveness of these filters is evident in various applications. For instance, in telecommunications, they help maintain clear voice and data transmissions. However, implementing dielectric filters requires careful consideration of the specific frequencies needed. Miscalculating this can lead to performance issues. It’s important to test configurations thoroughly to avoid any unwanted results.
Moreover, dielectric filters can be used in many environments. They are beneficial in laboratory settings and outdoor installations. Some users may overlook environmental factors like temperature or humidity. These elements can affect filter performance, leading to unexpected disturbances. Regular monitoring and adjustment are necessary, as consistency is key to achieving optimal signal quality.
Dielectric filters play a crucial role in enhancing signal quality. Their installation, however, requires careful attention to detail. Begin by identifying the appropriate location for your dielectric filter. Ensure it is placed near the signal source for optimal performance.
Select the proper dielectric filter based on the frequency range you are working with. According to industry reports, filters can reduce interference by up to 80%. This significantly improves signal clarity. Use tools like spectrum analyzers to assess signal strength before and after installation. This verification step can help reflect on your installation efficacy.
During installation, be cautious about the orientation of the filter. Incorrect alignment can lead to suboptimal performance. A high-quality dielectric filter can remove unwanted frequencies but may also introduce some loss. Monitor these losses closely.
Tips: Always check connections for any potential faults. Even minor issues can degrade performance. Regularly review your installation after a few weeks to identify any deterioration in signal quality. This reflection is key for ongoing improvement.
When using dielectric filters, attention to detail can significantly enhance signal quality. These filters are essential in various communication systems, as they allow specific frequencies to pass while blocking others. Operating them effectively requires careful consideration of a few best practices.
One important tip is to ensure proper alignment during installation. Misalignment can lead to poor signal quality. Double-check connections and mounting positions. Sometimes, a slight shift can cause signal degradation. Additionally, maintain a clean environment around the filter. Dust and contaminants can affect performance. Regularly inspect the filter and surrounding components for buildup.
Another key practice is to monitor temperature fluctuations. Dielectric filters are sensitive to temperature changes. Extreme heat or cold can alter their characteristics. Use temperature monitoring equipment to keep an eye on conditions. If the temperature exceeds or drops below ideal levels, consider recalibrating.
Lastly, keep an eye on signal interference. Nearby electronic devices can create noise that impacts signal clarity. Maintain some distance from potential sources of interference. Watch for patterns in signal quality that correspond with specific times of day or equipment usage. Adjusting your setup based on these observations can lead to better performance.
When using dielectric filters, issues can arise that affect signal quality. One common problem is signal loss. This often occurs due to improper installation or component mismatch. Check the connections and ensure everything is properly seated before assuming a fault with the filter itself.
Interference is another prevalent issue. External sources can disrupt your signals, leading to inconsistent performance. Keep the filter away from potential interference sources. You might need to experiment with placement. Sometimes moving cables can resolve unexpected issues.
Lastly, watch for fading signals. This might indicate that the filter is not suited for your specific frequency range. Performance may degrade over time, too. Regular inspection is vital. Don’t overlook the importance of clean components and connections. These little details can significantly impact functionality.
| Parameter | Description | Common Issues | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insertion Loss | The loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line | High insertion loss affecting signal clarity | Check connector integrity and return-loss measurements |
| Frequency Response | The variation of the output signal's amplitude and phase as a function of frequency | Poor frequency response leading to distortion | Conduct a frequency sweep to ensure performance across the operating band |
| Reflection Coefficient | A measure of how much signal is reflected back towards the source | High reflection causing signal loss | Verify matching network settings and re-tune if necessary |
| Isolation | The ability of a filter to reduce interference from other signals | Insufficient isolation leading to crosstalk | Inspect filter placement and consider alternative configurations |
| Temperature Sensitivity | How the performance parameters change with temperature variations | Fluctuating performance with temperature changes | Implement thermal management solutions to stabilize performance |






