Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
Dielectric filters play a crucial role in modern communication systems. These components are essential for frequency selection and signal clarity. They operate on the principle of dielectric resonance, allowing only specific frequencies to pass while blocking others.
According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global dielectric filters market is projected to reach USD 2 billion by 2026. This growth reflects the increasing demand for high-performance filters across various applications. The efficiency of dielectric filters contributes significantly to their popularity in telecommunications and aerospace industries. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions adds to their appeal.
However, the design of dielectric filters is complex. Engineers must carefully balance performance and manufacturing costs. Not all designs meet the required specifications, leading to potential issues in critical applications. This complexity prompts ongoing research to enhance efficacy further, emphasizing the need for innovation in dielectric filter technology.
Dielectric filters are optical devices designed to selectively transmit light. They are made from multiple thin layers of dielectric materials. These layers create a specific interference pattern, allowing certain wavelengths to pass while reflecting others.
The core principle of dielectric filters is transmission and reflection. When light hits the filter, some wavelengths are absorbed or reflected. The design determines which wavelengths are transmitted. This is crucial in applications like telecommunications, where specific light wavelengths are essential for data transmission.
Dielectric filters can be used in various fields, including photography and spectroscopy. However, their performance depends on precise manufacturing. Even slight imperfections can alter their effectiveness. This highlights the importance of quality control in producing these filters. Ensuring they meet specifications can be challenging, but it is vital for reliable performance.
Dielectric filters are essential components in modern optical and communication systems. They operate based on the principle of optical interference. Constructed from multiple layers of dielectric materials, they selectively transmit or block certain wavelengths of light. The design is often tailored for specific applications. These filters are crucial in devices such as lasers and sensors.
The working principle revolves around constructive and destructive interference. When light hits the layered structure, some wavelengths reflect while others are transmitted. This process depends on the thickness and refractive index of the layers. According to industry reports, dielectric filters exhibit a low insertion loss of typically less than 1 dB. They can achieve high transmittance levels, often exceeding 90% for certain wavelengths. However, the efficiency can vary with angle and polarization.
In real-world applications, imperfections in layer uniformity can introduce unpredictable results. Variations caused by manufacturing tolerances may lead to shifts in expected performance. Balancing manufacturing precision with cost remains a challenge. As industries demand higher precision, ongoing research aims to refine the fabrication processes. Such advancements promise to enhance the reliability of dielectric filters in diverse applications.
| Parameter | Description | Value/Range |
|---|---|---|
| Material | The dielectric material used in the filter | Ceramic, Glass, Polymeric |
| Frequency Range | Operational frequency bandwidth | DC to GHz |
| Insertion Loss | Power loss when signals pass through the filter | < 1 dB typical |
| Passband Ripple | Variation in passband gain | < 1 dB |
| Temperature Stability | Performance consistency over temperature variations | -40°C to +85°C |
| Q Factor | Quality factor indicating filter performance | > 1000 |
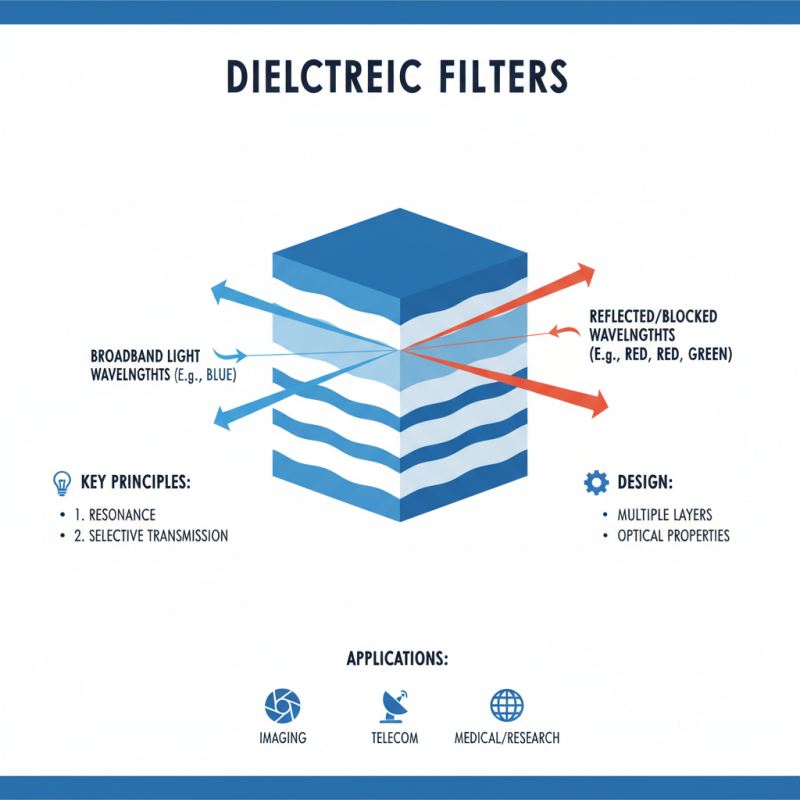
Dielectric filters are essential in various fields. They use the principles of resonance to selectively transmit certain wavelengths while blocking others. The design often includes multiple layers of dielectric materials, each crafted for its specific optical properties.
In telecommunications, dielectric filters are widely used. They help in separating different frequency channels. This is vital for maintaining signal clarity. In optical applications, these filters improve image quality by eliminating unwanted wavelengths. They are frequently found in cameras and telescopes.
Tips: Always consider the filter's bandwidth. A narrow bandwidth can be highly effective but might limit versatility. Think about the application. Choosing the right type matters greatly. Don’t overlook the potential for reflections and losses. These can affect performance more than you might expect.
Dielectric filters are essential in various applications. They offer significant advantages over other filter types. One major benefit is their superior selectivity. They can effectively separate multiple wavelengths. This ensures that desired signals pass through while unwanted ones are blocked.
Another advantage of dielectric filters is their minimal insertion loss. This means that they allow more signal power through. Many other filters can introduce significant losses, affecting overall system performance. Dielectric filters often operate over a broader bandwidth. This flexibility makes them suitable for a variety of uses.
They also provide excellent temperature stability. Changes in temperature can alter filter performance. Dielectric filters tend to maintain their characteristics better under varying conditions. However, some challenges exist. Designing dielectric filters can be complex. This complexity requires careful consideration and testing. The benefits, while clear, come with a need for precision in their application.
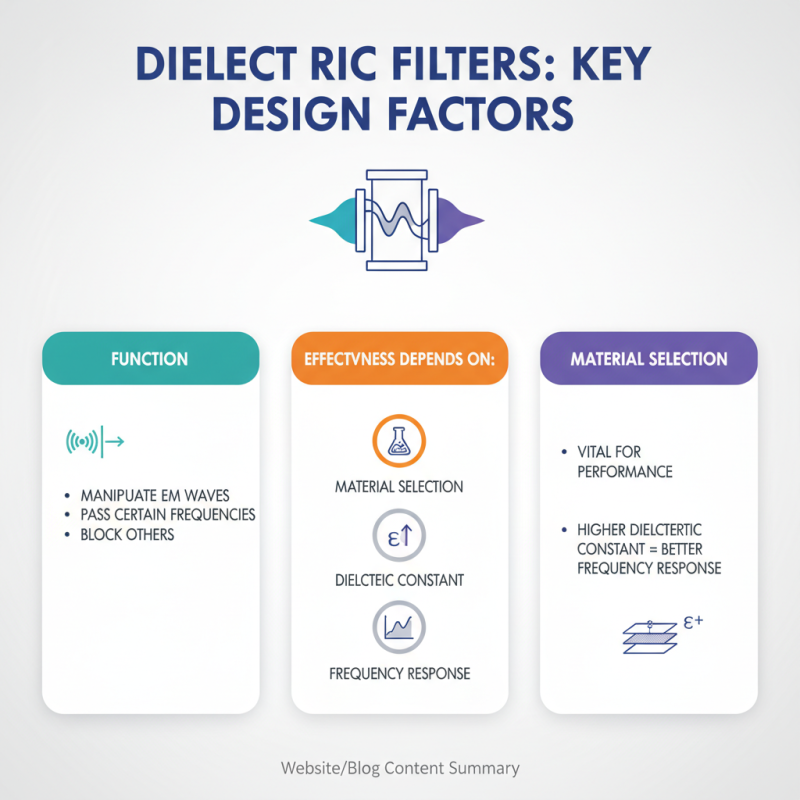
Dielectric filters are crucial in various applications. They manipulate electromagnetic waves, allowing certain frequencies to pass while blocking others. Their effectiveness largely depends on several design factors. Material selection is vital. The dielectric constant of the material influences filter performance. Higher dielectric constants often lead to better frequency response.
Layer thickness also plays a key role. Thinner layers can provide sharper cut-off frequencies. However, thinner layers may compromise the filter’s durability. Engineers must balance these aspects carefully. The quality of the dielectric material affects signal loss. Impurities can degrade performance, making material quality a priority in design.
Tips: When choosing a dielectric filter, consider the operating environment. Temperature fluctuations can change performance. Regular testing can identify issues early. Also, think about the intended application. A filter for communication may require different specifications than one for sensing.
In addition, fabrication methods influence the outcome. Different techniques can yield varied results. Reflecting on these methods can help improve future designs. Engaging with prototypes and getting feedback is essential for better refinements. Every decision in the design stage has a lasting impact on filter efficiency.






