Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
In the realm of optical technologies, selecting the appropriate dielectric filters can significantly impact the performance and efficiency of various applications. According to Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in photonics and dielectric materials, "The right dielectric filter not only enhances signal clarity but also ensures that the entire system operates optimally." This perspective highlights the critical nature of making informed decisions when it comes to dielectric filters, especially in fields ranging from telecommunications to biomedical imaging.
Choosing the right dielectric filters requires a comprehensive understanding of the specific application needs, including wavelength requirements, bandwidth, and environmental factors. As industries progress, the demand for customized solutions grows, making it essential to evaluate the numerous options available. Proper selection can lead to enhanced signal processing, reduced noise, and improved overall system reliability, underscoring the importance of making thorough assessments.
In this guide, we will explore the fundamental considerations for selecting dielectric filters, aiming to equip professionals with the knowledge necessary to choose the ideal components for their specific applications. By leveraging expert insights and practical criteria, users can navigate the complexities of the market and achieve optimal performance in their respective endeavors.

Dielectric filters are essential optical components used to selectively transmit or absorb certain wavelengths while reflecting others. The basic principle behind dielectric filters is the interference of light. These filters consist of multiple layers of dielectric materials, each designed to create constructive and destructive interference for specific wavelengths. When light interacts with these layers, certain wavelengths pass through, while others are reflected, allowing for precise control of light in various applications.
Understanding the functionality of dielectric filters is crucial for their effective implementation. They are commonly used in applications such as telecommunications, spectroscopy, and imaging systems. By tailoring the thickness and composition of each layer, manufacturers can design filters for specific bandwidths, enabling users to achieve desired outcomes in their projects. The performance of a dielectric filter is influenced by factors like incident angle, polarization, and environmental conditions, making careful consideration of these variables essential for optimal results.
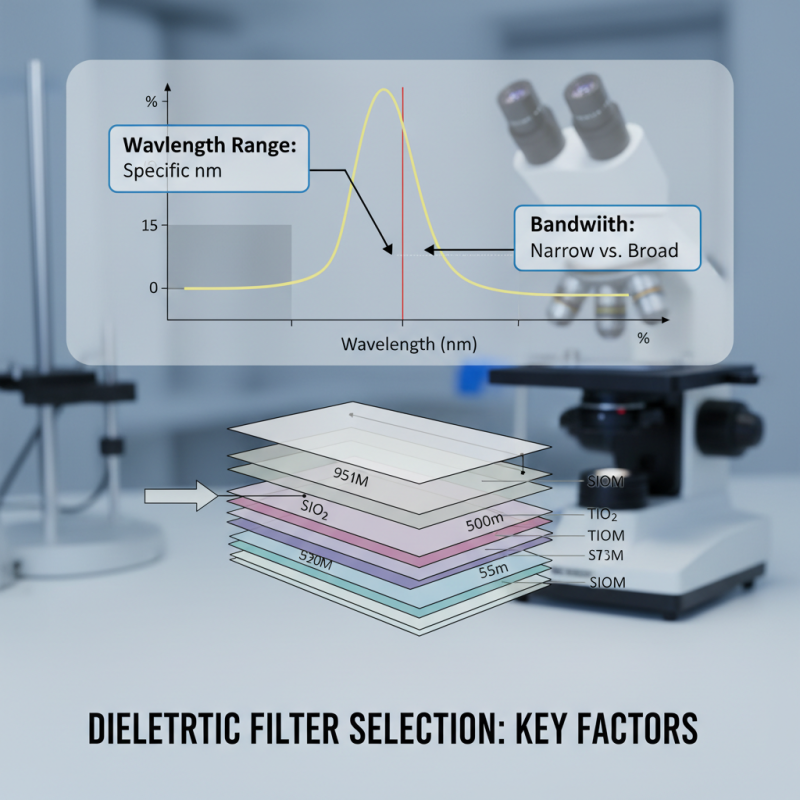
When selecting dielectric filters for specific applications, there are several key factors to consider to ensure optimal performance. First and foremost is the wavelength range the filter will operate within. Identifying the exact spectral range required for your application will help in narrowing down the options. Additionally, the filter's bandwidth is crucial; a narrower bandwidth can provide more precise filtering but may require a more complex design or higher cost.
Another important aspect is the quality of the filter, which is often assessed through parameters such as transmission efficiency and rejection ratio. High transmission efficiency ensures that the desired wavelengths pass through with minimal loss, whereas a high rejection ratio is vital for effectively blocking out unwanted wavelengths. Furthermore, examining factors such as temperature stability and polarization sensitivity can inform decisions based on the operating conditions of your application. By considering these key factors, you can select a dielectric filter that best meets your specific needs.
Dielectric filters are essential components in various optical applications, utilized for their ability to selectively transmit certain wavelengths while reflecting others. Different types of dielectric filters serve specific purposes tailored to various industries. For instance, bandpass filters are designed to allow a specific range of wavelengths to pass through, making them ideal for fluorescence microscopy, where the detection of specific emission wavelengths is crucial. According to a recent industry report by Research and Markets, the global market for bandpass filters is projected to reach a value of $3.1 billion by 2025, highlighting the growing demand in scientific research.
On the other hand, notch filters are designed to block specific wavelengths while permitting others, which is particularly beneficial in applications like spectral analysis and telecommunications. These filters help eliminate unwanted interference, thereby improving the accuracy of measurements and data transmission. The same report indicates that the telecommunications sector alone will account for a significant portion of the dielectric filter market, as the need for high-quality signal processing continues to rise. Moreover, dichroic filters, which reflect certain wavelengths and transmit others, are widely used in LED lighting and projection systems, optimizing performance by enhancing color purity and brightness.
Each type of dielectric filter offers unique advantages that align with specific application needs. Understanding these differences is vital for selecting the most suitable filter to ensure optimal performance in any given application. As the technology continues to evolve, staying informed about these advancements can help in making well-informed decisions for future projects.
When selecting dielectric filters for specific applications, it's crucial to assess various performance metrics to ensure optimal functionality. Key performance metrics include transmission efficiency, wavelength precision, thermal stability, and environmental resilience. According to a market report by Research and Markets, the demand for high-performance dielectric filters continues to rise, particularly in sectors like telecommunications and optical systems, where transmission efficiency can reach upwards of 95% under ideal conditions. Thus, understanding these metrics helps in choosing filters that not only meet the requisite technical specifications but also align with the environmental conditions they will encounter.
Another vital performance metric is the filter’s bandwidth, which is essential for applications that involve signal processing. A narrower bandwidth generally leads to better selectivity and reduced crosstalk between channels, which is critical in crowded frequency environments. Industry reports indicate that filters with bandwidths less than 1 nm are increasingly favored in advanced optical applications, as they enable greater signal clarity and system performance. Additionally, attributes such as temperature coefficients and mechanical durability play a significant role in the longevity and reliability of filters in dynamic operational settings. By systematically evaluating these performance metrics, engineers can enhance application effectiveness and ensure long-term operational stability.
By systematically evaluating these performance metrics, engineers can enhance application effectiveness and ensure long-term operational stability.
When integrating dielectric filters into your optical systems, attention to best practices can significantly enhance performance and longevity. First and foremost, it is crucial to ensure that the dielectric filters are properly aligned with the optical axis of the system. Misalignment can lead to increased losses and reduced efficiency; studies show that even a slight deviation can result in performance degradation of up to 30% in some applications. Additionally, implementing a cleanroom environment during installation and maintenance can prevent contamination that may affect filter effectiveness.
Regular maintenance is another key aspect of ensuring the long-term performance of dielectric filters. It is advisable to schedule periodic inspections and cleaning, especially in environments prone to dust and particulate accumulation. According to industry data, routine maintenance can optimize the lifespan of dielectric filters, with many systems showing a 20% improvement in operational stability when maintained regularly.
Tips for best practices include using specialized tools for cleaning that do not scratch filters and training personnel on proper handling techniques to avoid damage. Also, always refer to specific manufacturer guidelines for the storage and maintenance of dielectric filters to ensure they remain in optimal condition. This proactive approach not only enhances filter performance but also contributes to the overall reliability of the optical systems in which they are integrated.