Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
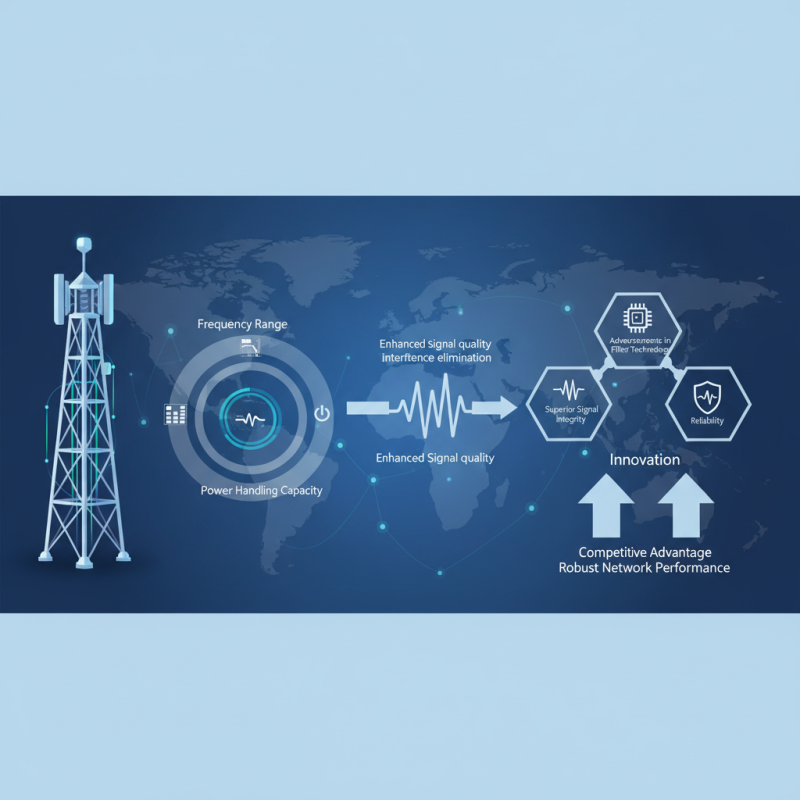
As we advance into 2025, the significance of Base Station Filters in ensuring optimal performance for communication networks cannot be overstated. These filters play a crucial role in enhancing signal quality by eliminating unwanted interference and improving the overall efficiency of base stations. With the rapid evolution of technology and an ever-increasing demand for bandwidth, selecting the right filters has become more critical than ever for telecommunications operators seeking to maintain competitive advantages and robust network performance.
In this guide, we will explore the key factors that influence the selection of Base Station Filters, including frequency range, insertion loss, and power handling capacity. Understanding these elements is essential for professionals aiming to make informed decisions that will enhance their network infrastructure. Furthermore, we will delve into the latest advancements in filter technology, highlighting how innovative solutions can lead to superior signal integrity and reliability. By the end of this discussion, readers will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to choose the most suitable Base Station Filters, ensuring their systems can meet the demands of modern communication environments.

Base station filters play a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability of communication networks. They are essential devices that help to eliminate unwanted frequencies and enhance the signals that truly matter for efficient data transmission. By reducing interference from adjacent channels, base station filters not only improve the clarity of communication signals but also enhance the overall capacity of the network. As technologies evolve, understanding the different types of filters and their specific applications becomes increasingly important for network operators.
When selecting the best filters, consider factors such as frequency range, insertion loss, and the filter's ability to withstand environmental conditions. Experts recommend conducting thorough research and possibly engaging with manufacturers to understand your network's specific needs. It’s important to ensure that the filters are compatible with the current equipment and future-proofed for technological advancements.
Tip: Regular testing and monitoring of the network performance can provide insights into the effectiveness of the filters in use. This practice can help identify potential issues early on, allowing for timely upgrades or replacements. Additionally, it’s wise to evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational efficiency, when making your selection.
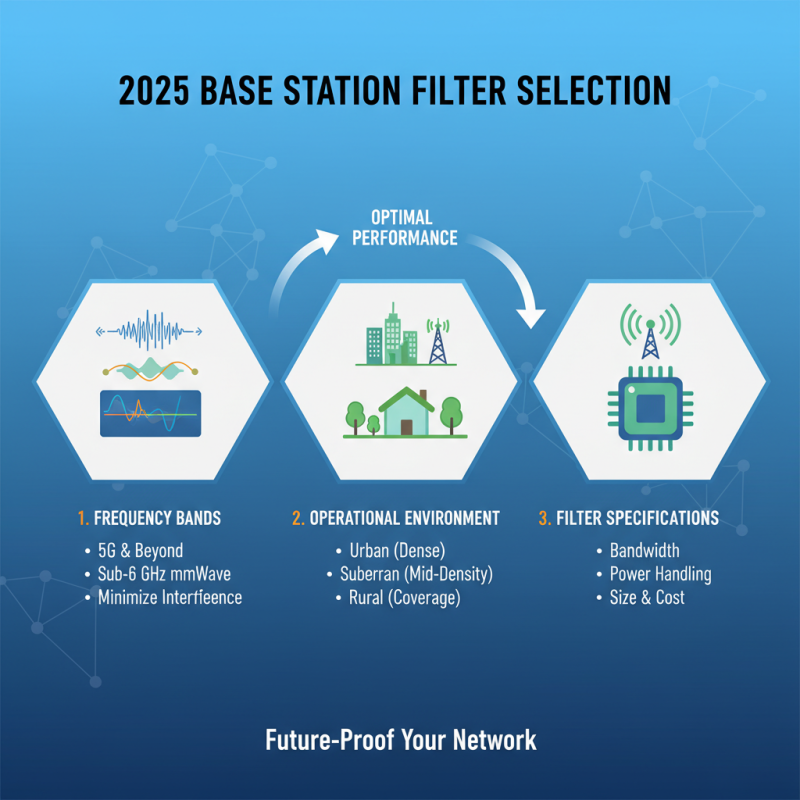
When selecting base station filters in 2025, it's essential to consider several key factors to ensure optimal performance. First and foremost, understanding the frequency bands that the filters will serve is crucial. With the ongoing evolution of telecommunications, different frequency bands may require specific filtering capabilities to minimize interference and enhance signal clarity. Analyzing the operational environment—whether urban, suburban, or rural—can help in determining the necessary specifications for your filters.
Another important factor to consider is the filter's insertion loss. This parameter indicates how much signal power is lost when passing through the filter, thus impacting overall system performance. Lower insertion loss is generally preferred, as it allows for more effective signal transmission. Furthermore, examining the filter’s power handling capacity will ensure it can withstand the maximum expected signal levels without distortion or damage. Additionally, evaluating the construction quality and reliability of the filters can prevent potential failures and extend their lifespan, thereby reducing maintenance costs in the long run.
Lastly, it’s vital to take into account the compatibility of the filters with other components within the base station setup. Ensuring that filters can integrate seamlessly with existing equipment can facilitate smoother operations and transitions during upgrades. Balancing these factors—frequency compatibility, insertion loss, power handling, and overall integration—will lead to more informed choices and improved performance for base station operations in the future.
When selecting base station filters, it's essential to understand the different types and their inherent advantages and disadvantages. Traditional low-pass filters are commonly used in base stations to allow desired frequencies to pass while eliminating higher-frequency noise. Their straightforward design offers good performance and is generally cost-effective. However, they might not be sufficient in complex environments where multiple signals coexist, potentially leading to interference issues.
On the other hand, band-pass filters can effectively isolate specific frequency ranges, making them ideal for applications requiring a narrow spectral focus. This precision can enhance signal clarity and reduce interference from other channels. However, band-pass filters often come with increased complexity and cost, making them less suitable for simpler applications. Additionally, the installation and tuning process of these filters can be more demanding, requiring specialized skills or knowledge. As such, the choice of filter should be guided by the specific needs of the base station and the operating environment, taking into account both the performance requirements and budget constraints.
This chart depicts the performance ratings of various types of base station filters. Each filter type is evaluated on a scale from 1 to 10, showcasing their effectiveness for optimal performance.
When selecting base station filters for optimal performance in 2025, evaluating specific performance metrics is crucial. Key metrics include insertion loss, return loss, and the filter’s ability to manage intermodulation distortion (IMD). According to a recent industry report by a prominent telecommunications research firm, filters with an insertion loss below 1 dB can significantly enhance signal integrity, which is essential for high-capacity networks. Moreover, maintaining a return loss greater than 20 dB can minimize signal reflections, thereby improving overall system efficiency.
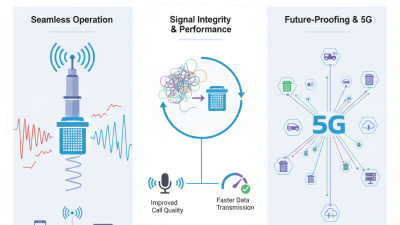
Tips for choosing the right filter include assessing the specific frequency bands your application requires, as filters are designed to optimize different spectrum ranges. Additionally, pay attention to the temperature stability of the components; filters that maintain performance across a wider temperature range tend to offer greater reliability in varying operational environments. Understanding the requirements of emerging technologies, such as 5G and beyond, will also guide your selection process, as these technologies demand higher performance standards from base station filters.
Ultimately, as the telecommunications landscape continues to evolve, ensuring that your filters meet these metrics will be vital for sustaining optimal performance. Regularly reviewing performance reports and industry advancements can provide insights into the best practices for filter selection, preparing your network for future demands effectively.
As the demand for higher data rates and efficient communication intensifies, the evolution of base station filter technology is pivotal for maintaining optimal performance in 2025 and beyond. Industry reports suggest that the global market for RF filters, including base station filters, is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of approximately 13.5% from 2023 to 2028, driven by the proliferation of 5G technology and the Internet of Things (IoT). This growth underscores the necessity for operators to integrate advanced filtering solutions that not only meet regulatory specifications but also enhance signal integrity across increasingly congested frequency bands.
Looking towards 2025, several key trends are likely to shape the landscape of base station filter technology. First, the shift towards integration—whereby multiple functions are implemented within a single chip—will streamline network components, reduce physical space requirements, and improve performance efficiency. Moreover, innovations in material science, such as the use of advanced ceramic and polymer materials, are expected to enhance filter performance, enabling higher power handling and improved thermal stability. Furthermore, as the rollout of 5G networks accelerates, filters that support millimeter-wave frequencies will become increasingly critical, necessitating a reevaluation of design approaches to accommodate higher bandwidth demands without compromising performance. These advancements indicate a future where intelligent filtering solutions will be central to achieving not only technical excellence but also sustainability in network operations.
| Filter Type | Frequency Range (MHz) | Insertion Loss (dB) | Power Handling (W) | Material | Expected Lifespan (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bandpass Filter | 700 - 800 | 1.5 | 100 | Ceramic | 10 |
| Low Pass Filter | 0 - 1000 | 0.8 | 200 | Aluminium | 8 |
| High Pass Filter | 1000 - 3000 | 1.0 | 150 | Stainless Steel | 12 |
| Notch Filter | 100 - 2000 | 2.0 | 75 | Plastic | 5 |
| Wide Band Filter | 600 - 3000 | 1.2 | 125 | Copper | 15 |