Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
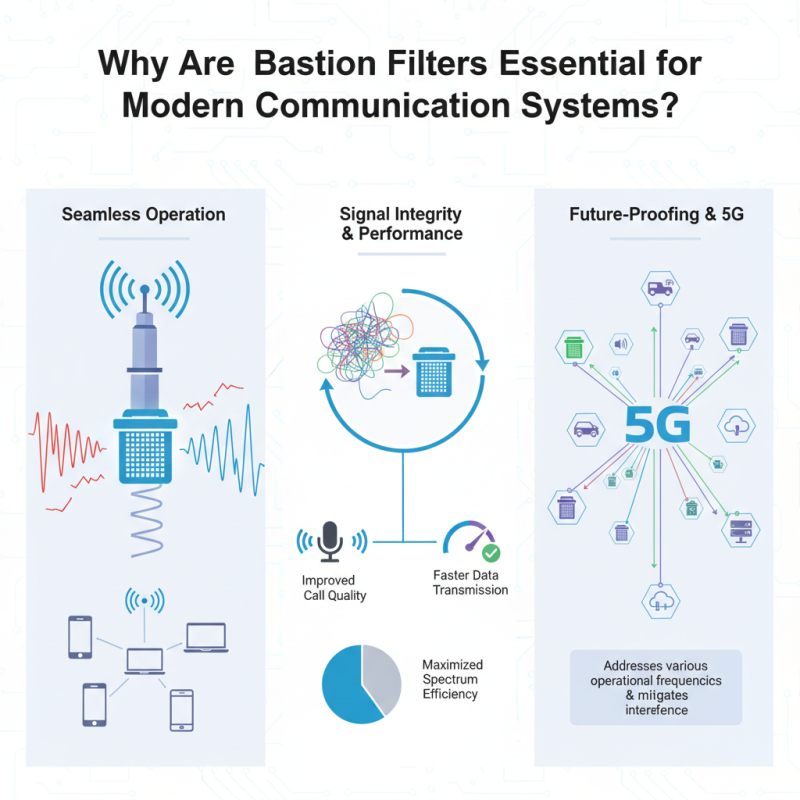
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern communication systems, the role of Base Station Filters has become increasingly vital. These specialized components are essential for ensuring the seamless operation of mobile networks, enabling high-frequency signals to transmit effectively while filtering out unwanted interference. As wireless communication demands grow exponentially, the functionality of Base Station Filters in managing signal integrity and enhancing overall network performance is of paramount importance.
Base Station Filters serve as the gatekeepers of signal processing, allowing for clearer communication by isolating desired frequencies from noise and potential disruptions. This capability not only improves call quality and data transmission speeds but also maximizes the efficiency of the available spectrum. As the number of connected devices soars and the need for reliable connectivity surges, the sophistication and deployment of Base Station Filters are crucial to meet these challenges head-on.
Moreover, with the advent of technologies such as 5G, the complexity of communication systems has intensified, making Base Station Filters indispensable in maintaining system stability and performance. By addressing various operational frequencies and mitigating interference, these filters play a critical role in the advancement of telecommunications, ensuring that modern communication systems can support the increasing demands of users worldwide.

Base station filters play a crucial role in modern communication systems, primarily by reducing signal interference that can degrade the quality and reliability of transmissions. Signal interference arises from various sources, including neighboring cell towers, electronic devices, and environmental factors. According to the Global Industry Analysts report, the market for radio frequency filters is set to exceed $3.5 billion by 2026, reflecting the critical need for effective interference management in increasingly congested urban environments.
Implementing high-quality base station filters can enhance network performance significantly. By ensuring that only the desired frequencies are transmitted and received, these filters minimize the risk of co-channel interference and adjacent-channel leakage. Research highlights that deploying advanced filtering solutions can improve overall signal quality by up to 30%, resulting in better voice clarity and faster data speeds for users across the network. For instance, in densely populated areas, where multiple communication systems operate in close proximity, the demand for reliable base station filters is imperative.
**Tips:** When selecting filters for your communication systems, consider not only the frequency range but also the filter's insertion loss and out-of-band rejection specifications. These factors will help ensure optimal performance and reduce potential interference. Additionally, it's wise to stay updated with advancements in filtering technologies that can enhance your network's resilience to interference as communication standards evolve.

Base station filters play a critical role in modern communication systems by managing the operational frequency ranges essential for effective transmission and reception of signals. Each communication system operates within specific frequency bands, which are regulated to prevent interference. The allocation of these frequency ranges is vital, as it ensures that various services can coexist without disrupting one another. For instance, cellular networks operate within distinct frequency ranges that must be precisely filtered to allow for clear communication and to minimize signal degradation.
The impact of frequency ranges on communication systems cannot be overstated. Different types of communication, such as mobile, satellite, and Wi-Fi, require filters that are tailored to their operational frequencies. These filters enable systems to maximize their bandwidth and enhance signal quality by eliminating unwanted noise and adjacent channel interference. Consequently, as the demand for higher data rates continues to grow, so does the need for advanced filtering solutions that allow communication systems to operate smoothly across overlapping frequency bands. This intricacy underscores the importance of base station filters in maintaining uninterrupted, high-quality communication in an increasingly interconnected world.
Base station filters play a critical role in modern communication systems, and their performance can significantly impact overall network efficiency. When assessing filter performance, two key metrics come to the forefront: insertion loss and rejection ratio. Insertion loss refers to the amount of signal power lost as the signal passes through the filter. A lower insertion loss value is desirable, as it indicates that the filter allows more of the desired signal to pass with minimal attenuation, thus enhancing the overall system performance.
On the other hand, rejection ratio measures the effectiveness of a filter in suppressing unwanted signals outside the desired frequency band. A higher rejection ratio signifies that the filter can effectively block or lessen interference from adjacent channels or noise sources, which is vital for maintaining communication clarity and quality. Both insertion loss and rejection ratio are crucial standards in designing and deploying base station filters, ensuring that modern communication systems operate seamlessly in increasingly congested frequency environments, thereby meeting user expectations for reliable and efficient service.
This chart illustrates the performance metrics of various base station filters, specifically focusing on Insertion Loss and Rejection Ratio. Lower insertion loss indicates better performance, while a higher rejection ratio signifies improved filtering capabilities.
Base station filters play a crucial role in the deployment and efficiency of 5G networks. As the demand for high-speed communication increases, the complexity of the radio frequency environment also rises. Base station filters are essential for ensuring that only the desired frequencies are transmitted and received at the base stations, thereby minimizing interference from other signals. This is particularly important in 5G networks, where the spectrum is more crowded due to the utilization of higher frequency bands.
The efficient functioning of base station filters directly impacts network performance by enhancing signal quality and increasing data transmission rates. By filtering out unwanted signals, these devices help to maintain a stable and reliable connection, which is vital for applications requiring low latency, such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery. Moreover, the integration of advanced filtering technologies optimizes energy usage within the network, allowing for a more sustainable communication infrastructure. As 5G continues to expand, the significance of base station filters will only grow, solidifying their place as integral components in modern communication systems.
| Filter Type | Frequency Range (GHz) | Insertion Loss (dB) | Rejection (dB) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diplexer | 1.8 - 2.6 | 0.5 | -30 | Cellular Networks |
| Bandpass Filter | 3.5 - 3.7 | 1.0 | -40 | 5G Networks |
| Notch Filter | 0.7 - 1.0 | 0.8 | -50 | RF System Protection |
| Low-pass Filter | DC - 2.0 | 1.2 | -60 | Base Station Output |
| High-pass Filter | 2.0 - 6.0 | 1.5 | -30 | Interference Mitigation |
Advancements in filter technology are set to play a pivotal role in enhancing connectivity for modern communication systems. As the demand for higher data rates and greater network efficiency continues to surge, innovative filter designs are emerging to meet these challenges. Notably, the integration of wideband and multi-band filter systems allows for simultaneous operation across various frequency bands, optimizing spectrum use and significantly improving overall network performance. This evolution is crucial as communication systems strive to deliver seamless and reliable connectivity in increasingly congested environments.
Furthermore, the ongoing miniaturization of filter components is facilitating the development of more compact and efficient base station designs. Smaller and more powerful filters can be integrated into advanced communication devices, allowing for a reduction in size without compromising signal quality. This trend not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of devices but also contributes to energy efficiency, which is becoming increasingly important in sustainable technology development. As we look forward, the continued research and innovation in filter technology will undoubtedly lead to a more interconnected and efficient communication landscape.